Moreover, booting in safe mode also increases the operational speed of the device as many features are restricted which results in less CPU usage. This can help you identify whether a problem is caused by a driver or by a piece of hardware. There are multiple ways you can boot your Windows 11 in safe mode. We are going to discuss the multiple ways in detail so stick around till the end.
Different Ways to Boot Windows 11 in Safe Mode
We will only be discussing the first type which is the most suitable for most users. Now, let’s take a look into the different ways we can boot Windows 11 in safe mode.
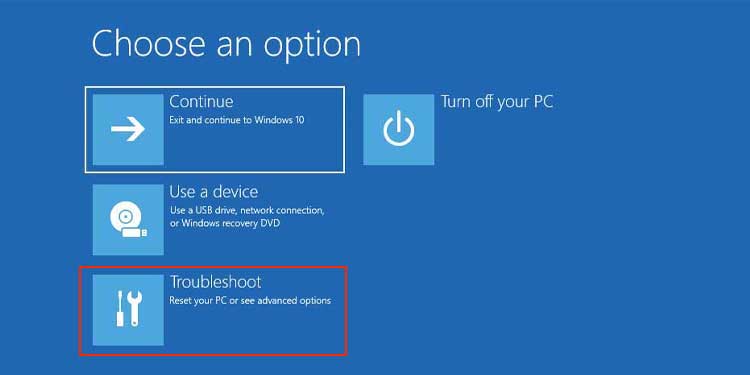
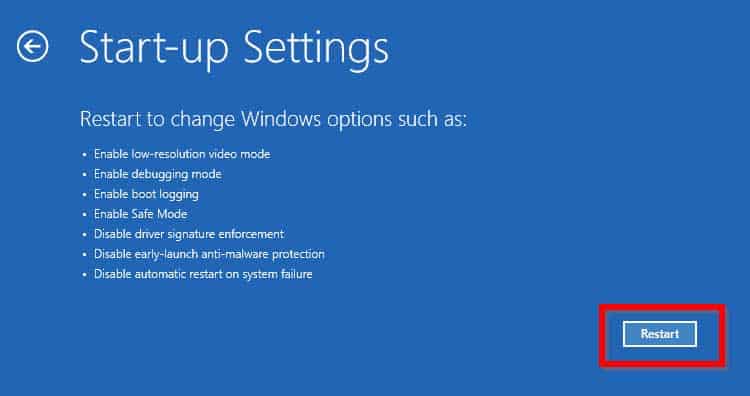
From the Login Screen
Users can boot their devices in Safe mode from the login screen without needing to log on to the PC. To do so, follow these steps.
From the Start Menu
You can also use the same procedure from the Start Menu. Let us explain in detail.
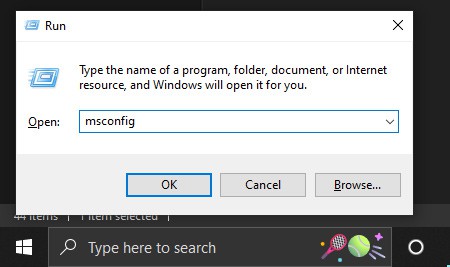
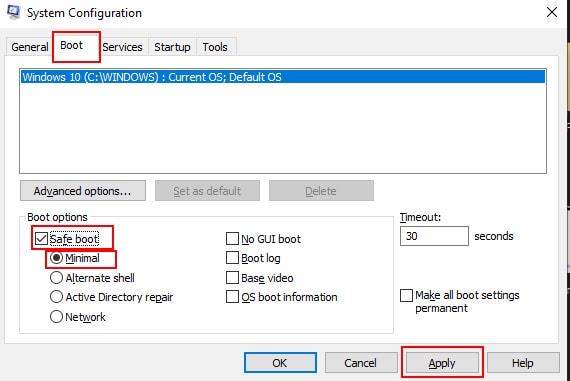
Using System Configuration
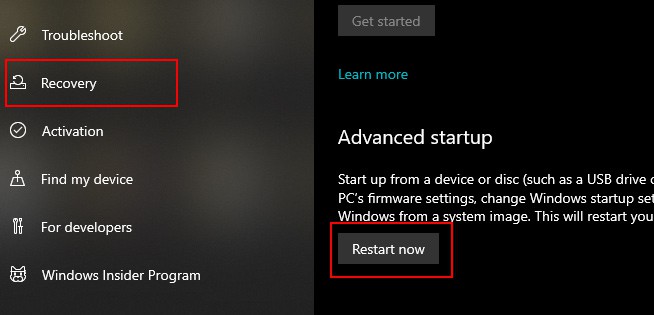
If you are already logged in to your PC, you do not have to restart your PC to boot up from the login screen as mentioned above. You can do it from the system configuration context. To do so, follow these steps.
From Settings
Users can also boot their PC in Safe mode from Settings. To do so follow these steps. On the next screen, you’ll see a list of options. Press 4 or F4 on your keyboard to boot into Safe Mode, or press 5 or F5 to boot into Safe Mode with Networking. Once your computer has booted into Safe Mode, you’ll see the Safe Mode logo in the corner of your screen. You can now troubleshoot your issue or run the program you need to.
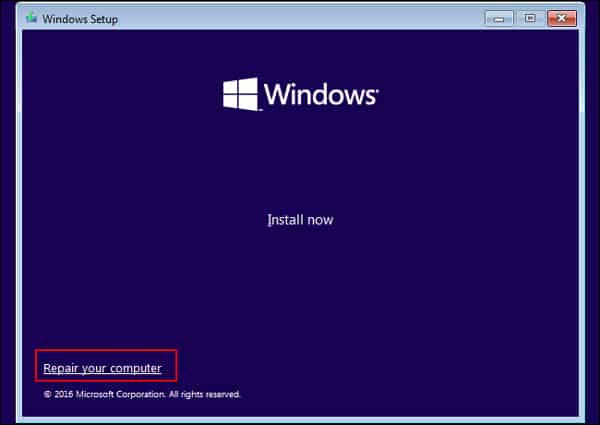
Using a Recovery Drive
A recovery drive can also enable you to boot your device in Safe mode. To do so, follow these steps.
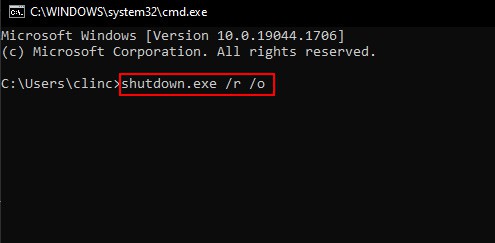
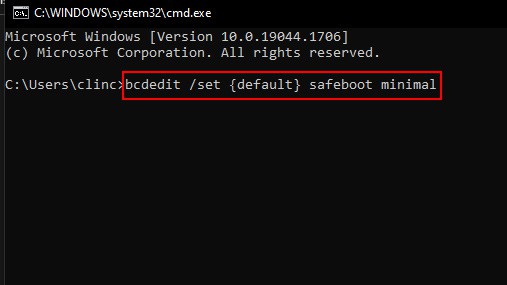
Using the Command Prompt
Command Prompt is a very handy tool that allows you to perform a number of technical tasks including booting your PC in safe mode. Follow these steps to do so. Alternatively, you can also choose the command prompt option from the advanced settings menu on the login screen. From then on follow these steps to boot your PC in safe mode. You can follow these command prompt procedures from Windows Recovery Mode or normal mode.