As long as network discovery is enabled, plugging in the Ethernet cables is often all that’s needed to connect Windows machines. Connecting Windows and Mac, or Windows and Linux, however, can get confusing. As such, we’ve detailed the steps to use Ethernet to connect and share files between various systems in this article.
How to Connect Two Computers With Ethernet
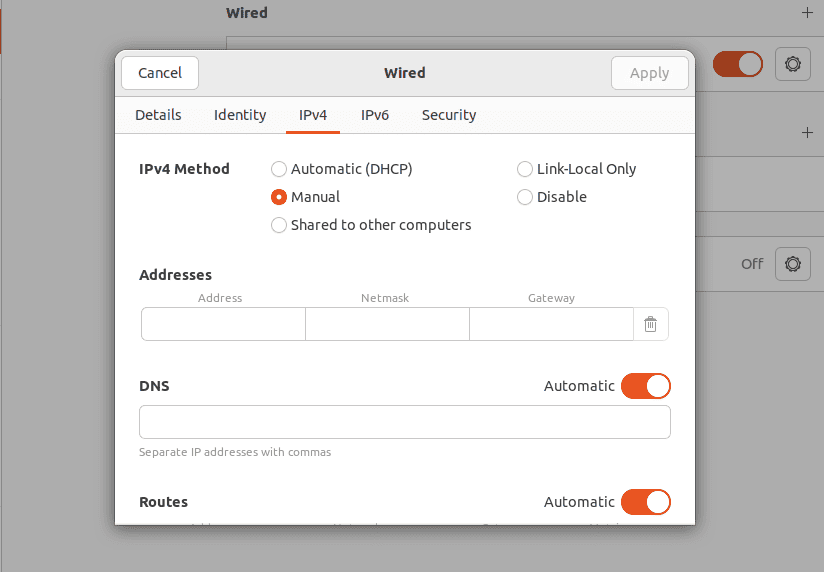
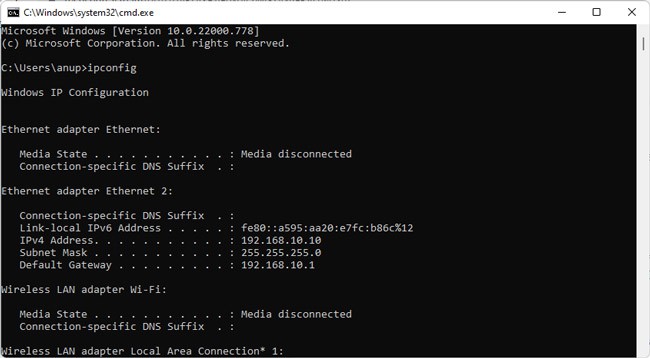
Physically connecting two computers with Ethernet is simple enough; you just plug the cord into the Ethernet ports on both computers. Certain Mac models don’t have Ethernet ports, though, in which case, you’ll need a USB to Ethernet adapter. Additionally, you can also connect two or more computers with a Switch. Regardless of the physical connection method, you’ll need to configure some basic networking settings before the computers can communicate with each other. When setting the Static IP as instructed in the sections below, use the following values: First Machine: IP 192.168.1.1, Subnet 255.255.255.0Second Machine: IP 192.168.1.2, Subnet 255.255.255.0
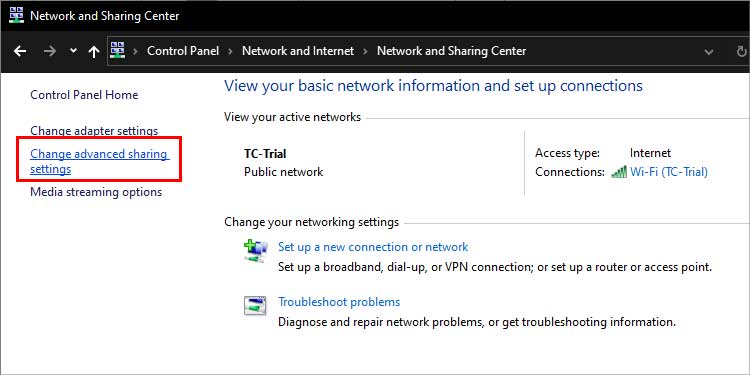
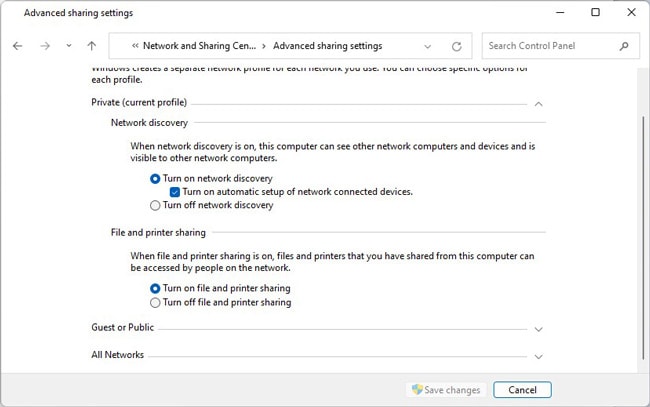
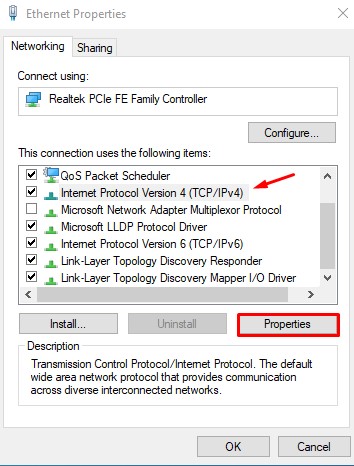
On Windows
Here are the steps for Windows systems:
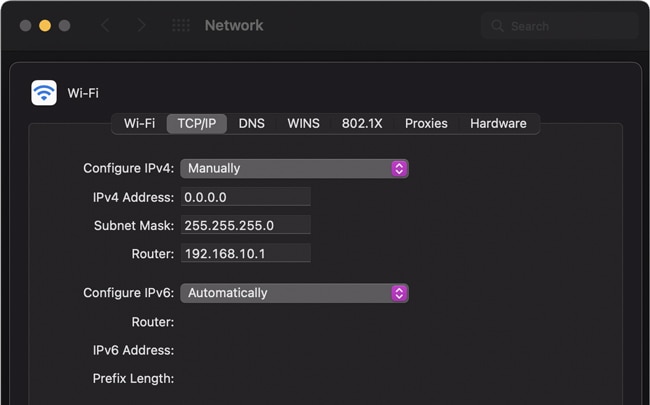
On Mac
Here are the steps to set a Static IP on Mac:
On Ubuntu
Here are the steps to set a Static IP on Ubuntu:
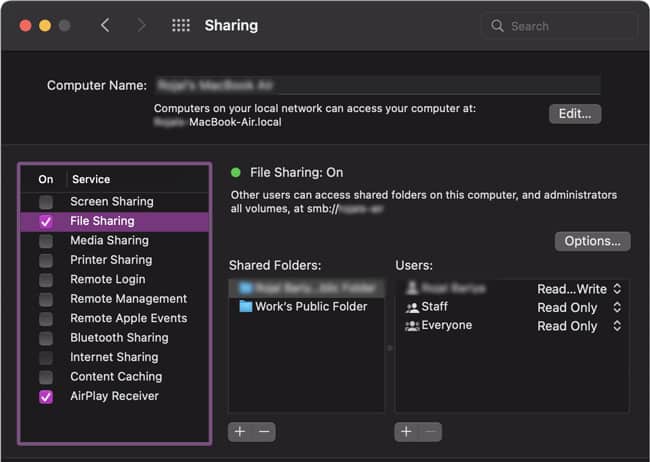
Transferring Files Between Two Computers
After configuring the network discovery and file sharing settings on the two computers, you can follow the steps listed below to share files.
Windows and Windows
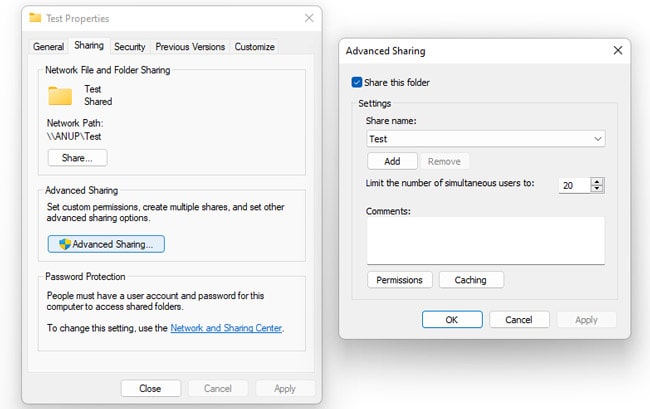
Here’s how to transfer files between two Windows computers with Ethernet:
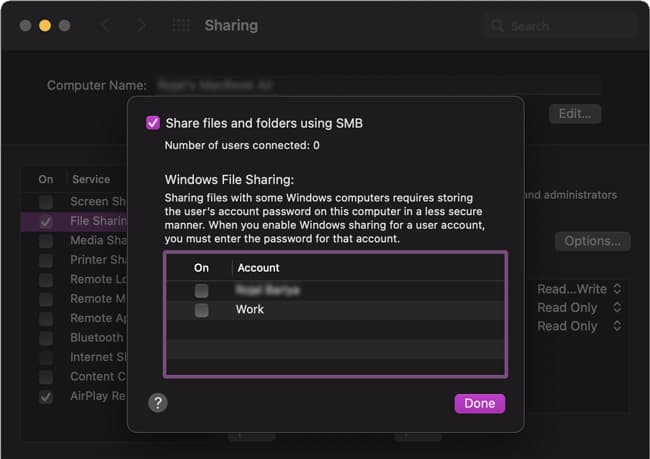
Windows and Mac
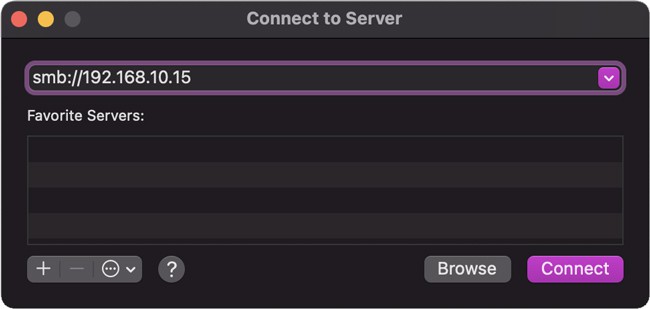
Here’s how to transfer files from Windows to Mac with Ethernet: If you want to transfer files from Mac to Windows instead, here’s what you should do:
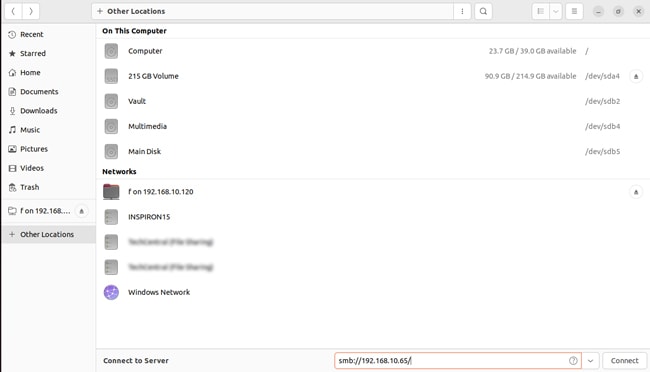
Windows and Linux
You can use the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol, which is built into most Linux distros, to transfer files between Windows and Linux. Here are the steps to do so on Ubuntu: